Energy-saving glass is a smart pick for today’s buildings. It cuts costs, keeps rooms cozy, and helps the planet. Numbers like U-value, SHGC, and VLT show how well it works. Features like Low-E coatings, insulated glass units (IGUs), argon gas, and vacuum glazing control heat and light. These lower heating and cooling bills. They also keep indoor temperatures steady and make your property worth more. This glass is great for homes, offices, and hospitals. Working with experts like GLASVUE gives you custom, top-quality glazing that fits your climate and meets green standards.
Why Is Energy-Saving Glass a Must for Modern Buildings?

Buildings today are more complex. Energy rules are stricter, too. That’s why energy-saving glass is so important. It’s not just about looking nice. It saves energy, makes spaces comfy, and is good for the environment.
Windows and doors can lose more than half of a building’s heat. This shows why good glass matters. It cuts costs and reduces harm to nature. From tall offices to hospitals, energy-saving glass makes buildings work better all year long.
Key Numbers for Energy-Saving Glass
To choose the right glass, you need to know some key numbers. These tell you how well the glass handles heat and light.
What Is U-Value?
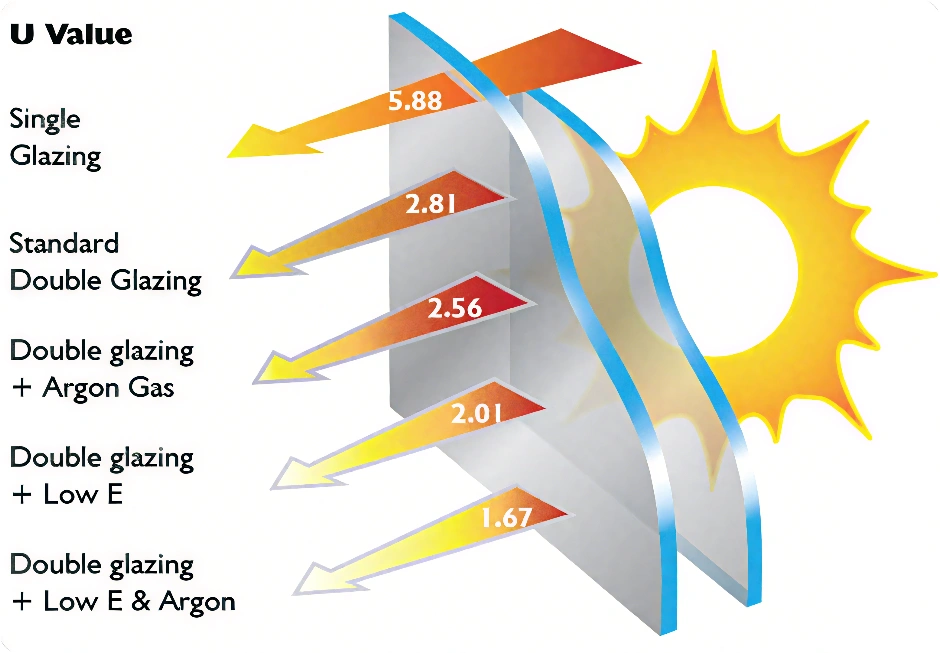
U-value shows how much heat moves through glass. It’s measured in watts per square meter per Kelvin (W/m²·K). A lower U-value means better insulation.
For example, regular single-pane glass might have a U-value of 5.5. But triple-glazed Low-E IGUs can get below 1.0. This kind of glass is used in energy-smart buildings, green homes, and fancy window systems.
As people focus more on saving energy in buildings, the U-value is a top number to check for meeting modern energy-saving rules.
What Is Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC)?
The Solar Heat Gain Coefficient, or SHGC, shows how much solar heat gets through a window or glass into a building. It includes sunlight that passes straight through and heat that the glass absorbs and then releases inside.
SHGC is a big deal for keeping spaces cool in hot weather. It helps make indoor areas comfy, especially in sunny or warm places.
What Is Visible Light Transmittance (Tvis)?
Visible Light Transmittance, or Tvis, measures how much visible light (from 380 to 780 nanometers) goes through glass. It affects how much natural daylight brightens a room.
Tvis is a percentage from 0 to 100%. A higher Tvis means the glass is clearer, letting in more light. This is great for bright rooms. A lower Tvis means less light gets through, which is good for privacy or shady designs.
In building design, Tvis helps balance sun shading with enough daylight. It affects how bright a room feels, how comfy it is to see, and how much energy you need for lights.
What Makes Energy-Saving Glass So Great?
Energy-saving glass uses smart ideas to work well. It’s not just one thing but a mix of features that give awesome results.
What Is Energy-Saving Glass?
This glass stops unwanted heat from moving in or out. But it still lets in plenty of natural light. It works in both cold and hot places. Low-E film cuts heat transfer between the glass and air. This reduces solar heat coming inside.
How Do Insulated Glass Units (IGUs) Help?
Less Heat Transfer:
Air or argon gas in IGUs conducts less heat than glass.
When warm or cool air tries to pass through, the gas layer slows it down.
Reduces Air Movement:
The gas inside IGUs is sealed in a closed space. This keeps it steady.
With the right thickness (usually 12mm to 16mm), the gas stops air from moving around, cutting heat transfer.
Why Are Low-E Coatings Important?
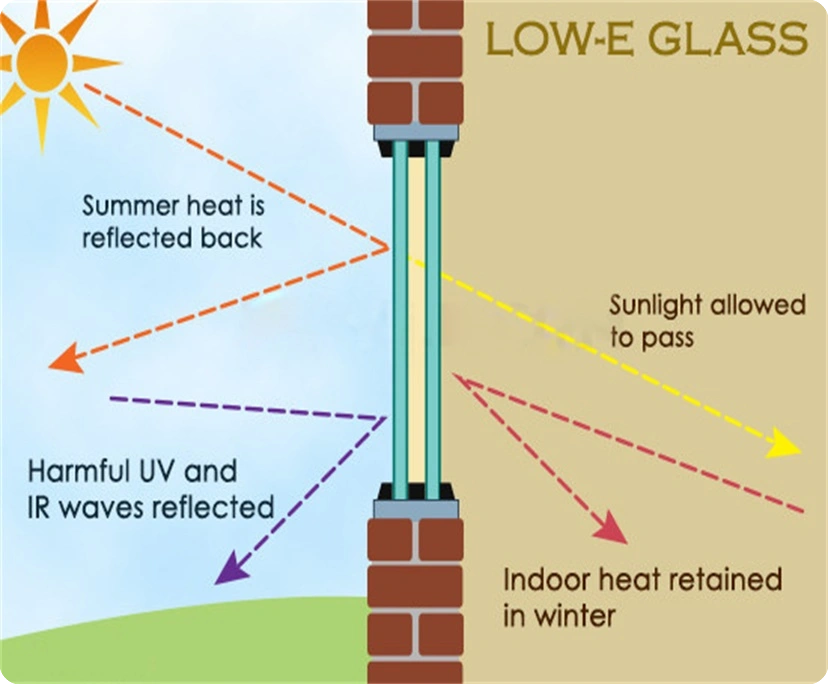
Low-emissivity coatings bounce infrared heat back inside during winter. In summer, they block heat from coming in. Regular glass has an emissivity of 0.84. But Low-E coated glass ranges from 0.08 to 0.15. This improves insulation without losing daylight.
How Do Solar Control Coatings Work?
These coatings push away the sun’s heat before it enters a building. They’re less helpful at night or in winter when keeping warmth inside matters. Heat-reflective glass acts like regular glass at night. It’s not great for cold places since it doesn’t hold heat well.
What Are Warm Edge Spacers?
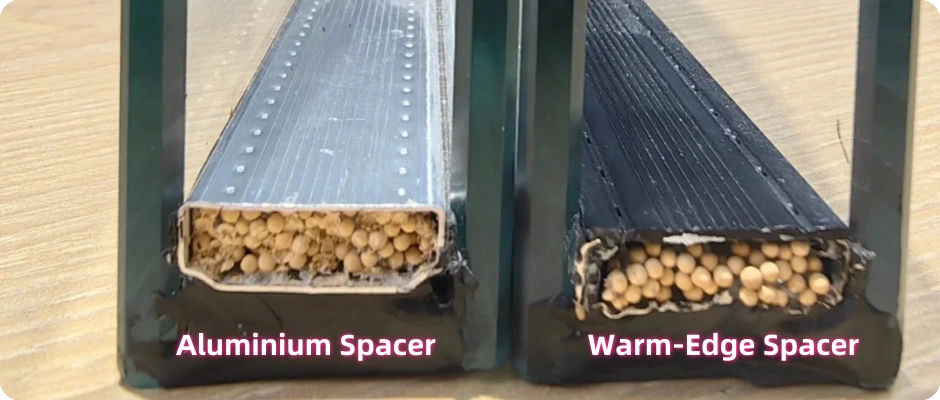

Warm edge spacers beat aluminum spacers for saving energy. Aluminum lets heat move easily, creating a “thermal bridge” that makes windows less efficient. Warm edge spacers, made from stuff like stainless steel with plastics, foamed polymers, or thermoplastics, don’t let heat pass as much. They lower the U-value of IGUs, boosting energy savings.
In cold or humid areas, aluminum spacers cause big temperature differences. This can lead to condensation or mold around glass edges. Warm edge spacers keep edges warmer, stopping condensation and helping the glass and frame last longer.
Why Use Argon Gas?
Argon gas slows heat movement in IGUs. It conducts less heat than air. Adding it boosts insulation, making rooms cozier and cutting heating and cooling needs.
What Is Vacuum Insulated Glazing?
Vacuum glazing removes all air between panes. This gives very low U-values. It’s perfect for harsh climates or buildings aiming for super-efficient standards, like passive houses.
How Does GLASVUE Help?

GLASVUE offers awesome solutions for modern buildings. They provide IGUs with argon gas, Low-E coatings, and warm edge spacers. They even have cool features like a glass you can control to change transparency. Their products pass tough tests, lasting over 50,000 cycles. Need fire resistance or clean surfaces for hospitals? GLASVUE delivers steady performance with little upkeep.
How Does Energy-Saving Glass Save Money?
This glass does more than make spaces comfy. It saves cash over time by cutting utility bills and raising property value.
Does It Lower Cooling Costs in Summer?
Yes, especially with Low-E glass that shades from the sun. It stops infrared heat before it warms a room. In summer, it blocks a lot of the sun’s heat, keeping spaces cool.
Does It Cut Heating Costs in Winter?
Yes, it keeps warmth inside with low-emissivity coatings. It also reduces heat loss through multiple panes or vacuum layers. Only a little heat escapes, keeping rooms warm.
Does It Improve Comfort All Year?
It keeps indoor temperatures steady. It stops drafts near windows. High-performance glass blocks much of the sun’s energy, preventing discomfort from heat. It also cuts glare while letting in good daylight.
Does It Boost Property Value?
Yes, energy-efficient upgrades are more popular now. Buyers and renters want lower costs and green features, making your property worth more.
Where Should You Use Energy-Saving Glass?
Energy-saving glass helps different buildings in special ways:
- Homes: It keeps heat in and cold out. This makes your home cozy and nice to live in.
- Offices: It manages heating and cooling needs. This lowers costs for air conditioning and heating.
- Public Places: It keeps indoor spaces steady and comfy. It also uses energy smartly.
In short, if you want comfort, lower energy bills, and to help the planet, energy-saving glass is a great choice.
Which IGU Setup Is Best for Your Area?
Choosing between double-pane argon-filled units or triple-pane vacuum designs depends on your climate. Is it more about heating or cooling? Different Low-E glass types fit different areas. High-transmittance glass is great for cold zones. Sun-shading glass works well in hot areas.
For expert help tailored to your project, GLASVUE’s insulated IGU solutions offer great support and know-how.
Why Is Energy-Saving Glass a Smart Long-Term Choice?
Picking the right glass does more than make a building look good. It keeps it running well for years:
- Choose wisely now, and your building stays cost-effective for its whole life.
- You’re not just saving on power bills. You’re protecting against rising energy costs.
- Work with expert makers like GLASVUE. They understand local needs and offer custom solutions for your building goals.
FAQ
Q1: Does energy-saving glass look different from regular glass?
A: No, it looks pretty similar in normal conditions. Some coatings might add a slight tint for style.
Q2: Do Low-E coatings reduce natural daylight?
A: Not always. Many Low-E glasses let in plenty of light while controlling heat well.
Q3: Is it worth replacing all windows with energy-saving units?
A: If you want long-term savings or green certifications like LEED or BREEAM, it’s a smart move.



