Low – E Glass , also known as low-emissivity glass has a thin metal/metallic oxide coating. It reduces UV and IR transmission while maintaining visible light transmittance, mainly cutting heat transfer through glass to boost building energy efficiency.
Certifications
ISO9001:2015 | ANSIZ97.1-2015 | AS/NZS2008:1996 | EN14449:2015+AC:2005
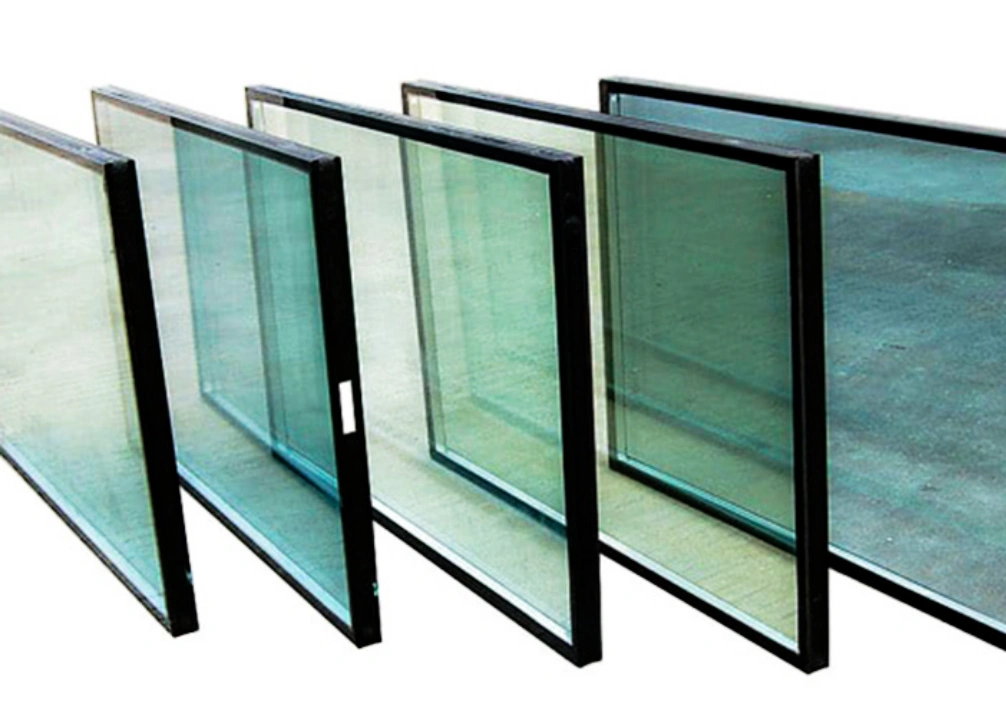

Glasvue can provide different types of Low – E glass. Moreover, we can offer various professional processing services to meet the requirements of your project.





Glasvue is committed to providing higher – quality Low – E glass products and cost – effective glass solutions for your construction projects.
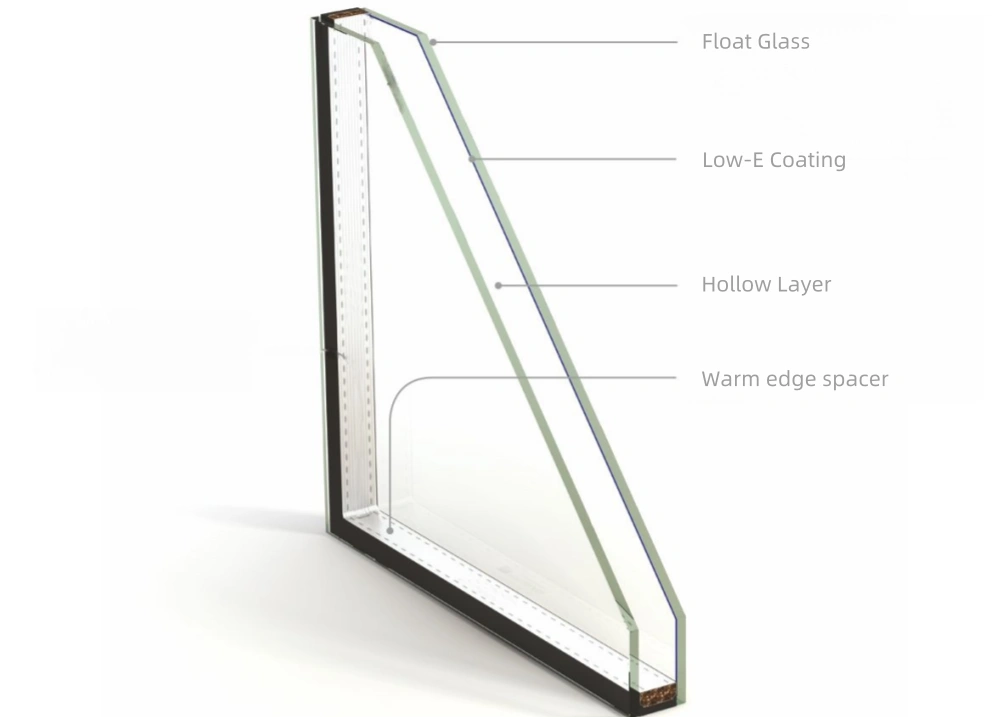
Low-E glass is made by coating a metal or compound film with low – emissivity function on the glass surface, and the low – emissivity functional layer is the metallic silver layer.
This film can efficiently reflect infrared rays, thereby reducing heat transfer, significantly lowering the glass’s emissivity and achieving the effect of heat preservation.
In addition, Low – E glass can also adjust the shading coefficient to meet the lighting requirements of different climate regions.
The bond between the glass and the interlayer ensures that, even when shattered, the glass fragments remain intact and do not scatter, significantly enhancing the safety of the glass.
The interlayer in laminated glass acts as a sound-dampening barrier, effectively reducing noise disturbances. Compared to traditional glass of the same thickness, it offers superior soundproofing performance.
Laminated glass demonstrates excellent thermal insulation properties, effectively minimizing heat exchange between indoor and outdoor environments, thereby reducing building energy consumption and conserving energy.


Our factory boasts an impressive 80% automation rate, minimizing human error while enhancing production efficiency and product uniformity. Rest assured, we guarantee the timely delivery of your orders.

Cold regions: A high Sc value (0.5 – 0.7) is preferred, which allows more solar radiation to enter, thus reducing heating costs.
Hot regions: A low Sc value (0.2 – 0.4) is advisable to minimize direct solar heat.
Cold regions: The #3 surface (the indoor – side surface), which preferentially reflects indoor heat back into the room.
Hot regions: The #2 surface (the outdoor – side surface), which blocks outdoor heat from entering.
Sealing problems: Polysulfide sealant has poor UV resistance, and silicone structural sealant should be used instead; the desiccant fails or is not filled adequately.
Structural defects: The absence of support strips causes the glass’s gravity to damage the sealant.
Experience the quality of GLASVUE glass firsthand with a complimentary sample tailored to your project requirements.
Let us design a glass solution that perfectly aligns with your unique architectural vision and technical specifications.
Access detailed technical data sheets for GLASVUE’s architectural glass products, including performance metrics and installation guidelines.
Gain inspiration from our curated collection of successful GLASVUE installations worldwide, showcasing innovative applications of architectural glass.
© All Copyright 2024 by GLASVUE | Privacy Policy